Health insurance benefits have been applied since November for a test method that simultaneously determines whether Helicobacter pylori infection, which is the first-degree cause of gastric cancer, and whether the bacteria are resistant to antibiotics.
Until now, such tests have been conducted by removing a small amount of the patient's gastric tissue with an endoscope and observing the cells under a microscope or by checking for genetic mutations in Helicobacter bacteria through gene polymerase chain reaction (PCR). However, the new test method, which has begun, can more clearly determine the presence of Helicobacter bacteria and antibiotic resistance in a short time using real-time PCR.
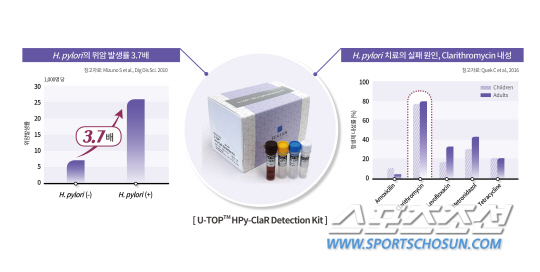
An official of SeaSun Biomaterials, who developed a new test product,'U-TOP Helicobacter clarithromycin detection kit', said, "This product is a product that can simultaneously determine whether Helicobacter bacteria are detected and possess Clarithromycin antibiotic resistance. "In particular, the test method for detecting Helicobacter bacteria was evaluated as a new technology, so the code was newly established."
Until now, it was possible to detect Helicobacter bacteria only with biopsy tissue collected immediately and to determine whether antibiotic resistance. The test was possible only when the bacteria were alive, and it took a long time for the culture test to determine the resistance to antibiotics.
On the other hand, SeaSun Biomaterials's Utop kit can check these test results in just two hours. In particular, there is no need to undergo a cumbersome gastric tissue biopsy (endoscopy), and the patient's past medical history can be estimated.
Park Hee-kyung, CEO of SeaSun Biomaterials said, "If the test method using the'U-TOP Kit' is activated, it will be possible to prevent gastric cancer through early detection, and it will be of great help in selecting an appropriate treatment." "We hope to become a leader in building a platform in this field by continuously developing genetic analysis techniques for faster and more accurate diagnostic tests and customized treatments."
Helicobacter bacteria, defined as carcinogens by the World Health Organization (WHO), are known to cause chronic gastritis, gastric ulcers, and gastric cancer while inhabiting the gastric mucosa of humans. It has been studied that the incidence of related diseases increases up to 5.3 times (3.7 times gastric cancer) due to high infection rates and recurrence rates in Asians including Koreans.
The Helicobacter infection rate of young gastric cancer patients is over 90%, which is significantly higher than those of the same age group, and it is reported that there is a high correlation between Helicobacter infection and gastric cancer.
In the antibacterial treatment to eradicate Helicobacter bacteria, in general, if the bacteria do not disappear after the first antibiotic treatment, the combination of the combined drugs is changed to enter the second treatment. Clarithromycin, which is mainly used for primary antibiotic treatment, has a steadily increasing resistance (close to 80%), so it is necessary to check the resistance to reduce drug costs, protect patients, and prevent the spread of resistance due to misuse of antibiotics.
Accordingly, from January this year, the Ministry of Health and Welfare has expanded the scope of government support for Helicobacter bacteria eradication treatment. Among Helicobacter infected patients, peptic ulcer, idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura, MALT lymphoma (a type of gastric cancer caused by mutations in the mucosal-associated lymphatic tissue), or early gastric cancer in patients undergoing endoscopic treatment are treated with related treatment drugs The salary is being applied.
관련 전문:
http://sports.chosun.com/news/utype.htm?id=201811100100091880006708&ServiceDate=20181109
http://www.mdtoday.co.kr/mdtoday/index.html?no=338214

